
How Steel Billet Production Impacts the Quality and Efficiency of High-Grade Steel Products
In the steel industry, Steel Billet Production plays a critical role in determining the quality and properties of the final steel products. Steel billets are intermediate products that are used as the base material for producing a wide range of products, including pipes, beams, and automotive parts. The precision and consistency with which these billets are produced can significantly affect the performance and quality of the final steel products. In this article, we will explore the key factors that influence Steel Billet Production and how they contribute to the overall quality of steel billets, offering insight into the production process and its impact on the steel industry.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Steel Billet Production Process
Steel Billet Production is a complex, multi-step process that begins with raw materials such as scrap steel or iron ore and ends with a high-quality steel billet ready for further processing. The process includes several critical stages, each of which influences the final product’s quality, including melting, casting, and rolling.
1.Selection and Preparation of Raw Materials

The choice of raw materials is one of the most important factors in Steel Billet Production. Steel can be made from either virgin ore or scrap metal, and each type has different impacts on the final product. Scrap steel, while more environmentally friendly and cost-effective, may introduce impurities that affect the billet’s quality. On the other hand, using iron ore in the production process requires high-energy consumption but produces cleaner billets.
Before the melting process, the raw materials are carefully sorted and prepared to ensure consistent composition and quality. The use of high-quality raw materials minimizes defects in the billets and enhances the mechanical properties of the final steel products.
2.The Melting Process

The next step in Steel Billet Production is melting. This is typically done in an electric arc furnace (EAF) or a blast furnace. The raw materials are heated to high temperatures to form molten steel, which is then subjected to various refining processes to remove impurities such as sulfur, phosphorus, and carbon. During this process, the steel’s chemical composition is adjusted to meet specific requirements for different types of steel products.
Energy efficiency is critical during the melting stage. Modern EAFs and blast furnaces use advanced technologies, such as oxygen injection, to reduce energy consumption and improve the quality of the molten steel.
3.Continuous Casting: The Key to Uniform Billets
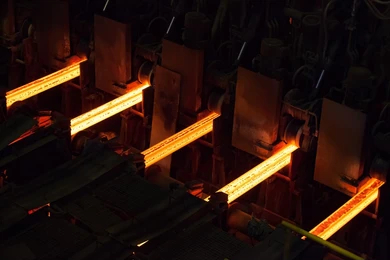
After the steel is melted, it is cast into billets using continuous casting machines. Continuous casting is a more efficient method than traditional casting, as it reduces the cooling time and minimizes the risk of defects such as cracks or porosity in the billets.
In this process, the molten steel is poured into molds and cooled gradually to form a solid shape. The billets are then cut to a specific length, depending on the required specifications for further processing.
The quality of the continuous casting process has a direct impact on the structural integrity of the billets. A smooth casting process minimizes surface defects and ensures uniform composition, which is critical for producing high-quality steel billets that meet the needs of end-users.
Factors Influencing the Quality of Steel Billet Production
The production of high-quality billets requires precision and control at every stage. Several factors can impact the quality of Steel Billet Production, including temperature control, cooling rates, and the presence of impurities.
1.Temperature Control
Temperature plays a crucial role in Steel Billet Production. The temperature of the molten steel during the melting and casting processes must be carefully controlled to avoid defects in the billets. Too high a temperature can lead to excessive oxidation, while too low a temperature can cause solidification defects. Maintaining the correct temperature ensures that the billets are uniform and free from cracks or other structural flaws.
Advanced temperature control systems have been developed to monitor and adjust the heat levels in real-time, allowing manufacturers to maintain consistent billet quality throughout production.
2.Cooling Rates and Solidification
The cooling process also significantly impacts the quality of steel billets. Rapid cooling can cause thermal stresses in the billets, leading to cracks or distortion. On the other hand, slow cooling can result in the formation of coarse grains, affecting the billet’s mechanical properties.
Steel Billet Production relies on precise control of cooling rates during solidification to prevent these issues. Some facilities use water-cooled molds or advanced cooling techniques, such as air misting, to control the cooling speed and avoid defects in the billets.
3.Impurities and Alloying Elements
The presence of impurities and alloying elements can affect the quality of the billets. Common impurities such as sulfur, phosphorus, and carbon can weaken the steel and affect its performance in later stages. To ensure the quality of Steel Billet Production, refining processes such as ladle refining and vacuum degassing are used to remove these impurities.
In addition, alloying elements such as chromium, nickel, and manganese may be added to enhance the properties of the steel. These elements improve the steel’s strength, resistance to corrosion, and ability to withstand high temperatures. The precise control of alloying elements is essential to meet the specific performance requirements for different steel products.
Optimizing Steel Billet Production for High-Quality Results
1.Automation and Control Systems
To achieve high-quality billets, manufacturers have increasingly adopted advanced automation and control systems. These systems provide real-time monitoring of every stage of the Steel Billet Production process, allowing for immediate adjustments to optimize production quality. Automated systems track critical parameters such as temperature, pressure, and alloy composition, ensuring that each billet meets the required specifications.
2.Quality Control and Testing
Quality control is an essential part of Steel Billet Production. After the billets are produced, they are subjected to various testing methods, including mechanical testing, chemical analysis, and visual inspection, to ensure they meet industry standards. Non-destructive testing methods such as ultrasonic testing and X-ray inspection are used to identify defects in the billets that may not be visible to the naked eye.
Through rigorous quality control and testing, manufacturers can identify any issues early in the production process and correct them before the billets are further processed into finished products.
The Future of Steel Billet Production
The future of Steel Billet Production is likely to see continued advancements in automation, energy efficiency, and sustainability. As the demand for high-quality steel products increases, manufacturers will need to adopt more efficient and environmentally friendly production techniques.
In addition to energy-saving technologies, innovations such as 3D printing and smart manufacturing are likely to play an increasing role in billet production. These technologies will enable manufacturers to produce billets with even greater precision and customization, meeting the evolving needs of industries such as automotive, construction, and aerospace.
The Crucial Role of Steel Billet Production in Steel Manufacturing
Steel Billet Production is a fundamental process that lays the foundation for the production of high-quality steel products. By optimizing each stage of production, from raw material selection to continuous casting and cooling, manufacturers can ensure that the billets produced meet the highest standards for strength, durability, and performance. As the steel industry continues to evolve, innovations in technology and process control will further enhance the quality and efficiency of Steel Billet Production, meeting the growing demand for superior steel products across industries.






